What is Eco-Friendly Leather Made From?

Eco-friendly leather is made from plant-based materials like pineapple leaves, apple peels, mushroom mycelium, cactus, and coconut waste. These materials are crafted into leather alternatives that mimic the look, feel, and durability of traditional leather but avoid the environmental and ethical issues associated with animal-based and synthetic leather.
Key Points:
- Materials Used: Pineapple leaves (Piñatex), apple peels, mushroom mycelium, cactus (Desserto), and coconut waste (Malai).
-
Advantages:
- Reduces agricultural waste by repurposing by-products.
- Uses fewer resources like water and energy.
- Avoids harmful chemicals like chromium used in traditional tanning.
- Biodegradable and less polluting than synthetic leather.
- Applications: Handbags, shoes, wallets, belts, home décor, and travel gear.
- Production Process: Utilises safe, eco-conscious techniques like fermentation, natural binding agents, and solar drying.
Eco-friendly leather not only offers a cruelty-free option but also addresses pollution, waste, and resource inefficiency in the leather industry. Choosing these alternatives supports better practices for the planet and local economies.
The Future of Fashion | Leather Made From Fruits, Vegetables & Grains!
Plant-Based Materials for Eco-Friendly Leather
New plant-based materials, crafted from agricultural leftovers and renewable resources, are paving the way for eco-friendly, durable, and stylish leather alternatives. These innovative options are not only reducing environmental impact but also offering exciting opportunities for sustainable design.
Pineapple Leaves (Piñatex)
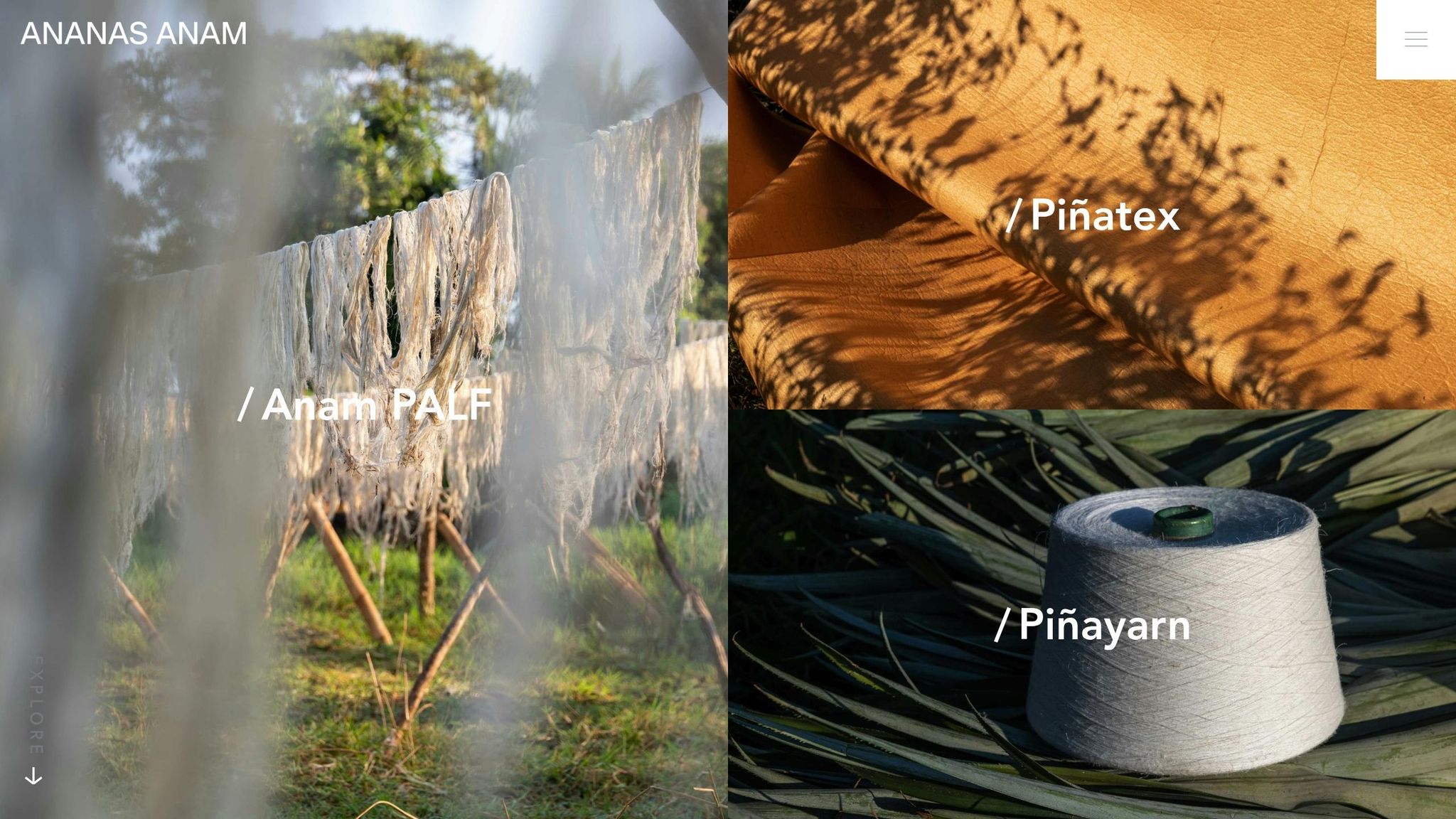

Piñatex is created from the fibres of pineapple leaves, a by-product of pineapple farming. This process not only reduces agricultural waste but also provides an additional source of income for farmers. The resulting material is flexible, strong, and ideal for crafting handbags, footwear, and even upholstery.
Apple Peels
Apple leather is made by repurposing apple pomace - what’s left after apples are juiced - into a flexible, leather-like material. This approach helps tackle food waste while offering a natural, textured material that’s perfect for accessories and small leather goods.
Mushroom Mycelium
Derived from mushroom mycelium grown on agricultural waste, this material closely resembles traditional leather in texture and durability. Its production process is resource-efficient, and the material itself is breathable, making it a promising option for eco-conscious fashion.
Cactus Leather (Desserto)
Cactus leather comes from the leaves of the Nopal cactus, a plant that requires minimal water to grow. The harvesting process is sustainable, allowing the cactus to regenerate naturally. This makes it an excellent choice for regions where water is scarce, while its durability suits a variety of applications.
Coconut Waste (Malai)
Malai is a leather alternative made from coconut processing by-products, such as coconut water and fibrous waste. The resulting material has natural antimicrobial properties and absorbs dyes effectively. This process not only reduces waste but also supports local coconut farmers and boosts regional economies.
These plant-based materials highlight a growing shift towards sustainable leather production. By minimising waste and embracing circular economy principles, they represent a significant step forward in creating eco-conscious alternatives for the leather industry.
Production Processes and Benefits
Plant-based materials are turned into eco-leather through environmentally conscious and high-quality methods. These processes mark a shift from traditional leather production, offering a more sustainable alternative. Everything starts with responsibly sourced materials, ensuring minimal waste and maximum efficiency.
Raw Material Sourcing
The journey of plant-based leather begins with renewable resources that would otherwise go to waste. By using agricultural by-products, this industry not only minimises waste but also creates additional value.
For example, pineapple leaves, left over after fruit harvesting, are collected without requiring extra land or water. This not only prevents waste but also provides farmers with an additional income stream. Similarly, mushroom mycelium is grown in controlled environments using agricultural residues like hemp stalks, corn husks, and sawdust - contributing to a circular economy. Cactus plants are harvested sustainably, with only mature parts collected, allowing the plant to regenerate naturally.
Processing Methods
The production of plant-based leather avoids harmful chemicals, focusing on safer and more eco-friendly techniques. Natural binding agents replace the toxic substances commonly used in conventional leather tanning, making the process safer for both workers and the environment.
For instance, mycelium leather relies on fermentation. Under controlled conditions, mycelium grows into dense, leather-like sheets without the use of harmful solvents or heavy metals. Other materials undergo mechanical processes such as grinding, pressing, and the application of natural resins. In the case of apple leather, apple pomace is dehydrated at low temperatures and combined with natural polymers to create flexible sheets, which also saves energy. Solar drying methods further reduce reliance on energy-intensive industrial dryers. Throughout the process, strict quality controls ensure durability and flexibility without compromising sustainability.
Measurable Benefits
Compared to traditional leather production, plant-based leather offers clear environmental advantages. It significantly lowers carbon emissions, reduces energy use, and maintains a high standard of durability and aesthetics.
By reusing agricultural water and adopting energy-efficient methods like natural drying, the process consumes fewer resources overall. The absence of harsh chemicals, such as chromium and formaldehyde, ensures safer products and healthier communities.
One standout benefit is biodegradability. Unlike synthetic alternatives, plant-based leathers decompose much faster, aligning with circular economy principles and reducing landfill waste. Additionally, the use of agricultural by-products not only reduces waste but also creates new income opportunities for farming communities.
sbb-itb-8c9b0a3
Uses in Fashion and Lifestyle Products
Plant-based leather has made its mark in the fashion and lifestyle industry, blending eco-consciousness with everyday utility. These materials are proving that sustainability and style can work hand in hand, offering a practical and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional options.
Fashion and Lifestyle Applications
Plant-based leather is becoming a go-to material for handbags, purses, and structured bags, thanks to its flexibility and durability. Designers have found that mycelium leather can be shaped into detailed designs, while apple leather provides a smooth, refined finish ideal for clutches and evening bags.
In footwear, these alternatives are gaining traction for their comfort and aesthetic appeal. Cactus leather, for instance, is a popular choice for formal shoes and boots, offering both natural texture and breathability. Pineapple leather, on the other hand, is lightweight, making it a great option for casual trainers and sandals.
Wallets and smaller accessories also benefit from these materials. Coconut waste leather, for example, delivers a consistent texture that ensures clean edges and precise stitching, while its unique patterns offer a distinctive look compared to synthetic options.
Belts and straps crafted from plant-based leather stand out for their strength and ability to develop a subtle patina over time, adding character to the product.
In home décor, items like cushion covers, table mats, and decorative panels showcase the natural variations in colour and texture that plant-based leather offers. Apple leather, with its smooth surface, is particularly well-suited for items that require frequent cleaning, combining practicality with elegance.
Travel gear, including laptop bags, luggage, and organisers, benefits from the moisture-resistant properties of materials like cactus leather, which perform well in different weather conditions. These versatile applications highlight the growing potential of plant-based leather in replacing conventional materials.
Comparison with Other Leather Types
When compared to traditional and synthetic leather, plant-based alternatives stand out for their durability, ease of maintenance, and environmental advantages. While synthetic leather may sometimes be easier to clean, it often falls short in breathability and eco-friendliness. As production techniques evolve, plant-based leather continues to prove itself as a sustainable and stylish choice for a range of lifestyle products.
Fit for Indian Lifestyles
Plant-based leather aligns perfectly with India's climate and values. Materials like pineapple leather, with their breathable qualities, are ideal for hot summers, while moisture-resistant options such as cactus leather are well-suited for the monsoon season.
Culturally, these eco-friendly options resonate with the principle of ahimsa (non-violence) and the growing demand for products that avoid animal harm. Additionally, using agricultural by-products like pineapple leaves, coconut waste, and apple remnants supports the tradition of reducing waste and opens up opportunities for local production.
The versatility of plant-based leather makes it suitable for both modern and traditional Indian fashion. Whether it's sleek office bags for the workplace or accessories that complement heritage attire, these materials offer a balanced mix of style and practicality to meet the needs of today’s consumers.
The GreenHyde's Approach to Eco-Friendly Leather
The GreenHyde is redefining the eco-leather market in India by combining sustainable materials with innovative production techniques. By merging traditional craftsmanship and plant-based alternatives, the brand is carving a niche in India's sustainable fashion space. Its focus lies on ethical manufacturing and environmental care, setting an example for the industry.
Plant-Based Materials Used
The GreenHyde transforms agricultural waste into high-quality leather alternatives, adhering to rigorous ethical, sustainable, and performance standards. This dedication to sourcing plant-based materials serves as the backbone of their eco-conscious designs.
Ethical Craftsmanship and Design
Every product crafted by The GreenHyde reflects their commitment to sustainability. Their detailed, handcrafted creations are a testament to their environmentally conscious methods. As they put it:
"Our plant-based creations honour refined craft, thoughtful innovation, and the natural beauty of sustainable design." - The GreenHyde
Conclusion
Eco-friendly leather is reshaping the way we think about sustainable fashion. By turning to plant-based sources, it addresses many of the issues tied to traditional and synthetic leather production.
Key Points
Eco-friendly leather stands out for its use of renewable materials and the repurposing of agricultural waste. This not only supports more sustainable manufacturing practices but also offers durability and style that rivals conventional leather.
These materials are incredibly versatile, finding their way into handbags, wallets, home décor, and travel accessories, proving their relevance across various lifestyle products.
What’s more, utilising agricultural waste not only helps the environment but also creates additional income opportunities for farmers, making it a win-win solution.
Making Better Choices
Choosing eco-friendly leather empowers you to align your purchases with both your style and your values. Every decision you make as a consumer can support brands that prioritise sustainability and ethical practices, driving positive change.
Take The GreenHyde, for example. This brand shows that responsible manufacturing and high-quality, stylish products can go hand in hand. Each purchase becomes a step toward environmental responsibility without sacrificing aesthetics or functionality.
FAQs
How durable and easy to maintain are plant-based leather alternatives compared to traditional leather?
Plant-based leather alternatives are built to stand the test of time, offering durability similar to traditional leather. With proper care, these materials can last 5 to 10 years. They’re often water-resistant and stain-resistant, requiring little upkeep - usually just a quick wipe with a damp cloth. This makes them a practical and environmentally friendly option for everyday use.
While lower-quality versions might crack or peel over time, premium plant-based leathers - crafted from materials like pineapple leaves, mushroom mycelium, or cactus - are designed for longevity. To keep them in good shape, avoid exposing them to excessive heat or moisture, much like you would with traditional leather products.
What are the benefits of using agricultural waste to make eco-friendly leather?
Using agricultural leftovers to create eco-friendly leather offers several environmental perks. For starters, it helps minimise waste by turning materials like pineapple leaves, apple peels, or cactus fibres - things that often end up in landfills or are burned - into something useful. This not only reduces waste but also helps lower air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, this method encourages responsible resource use by opting for renewable, plant-based materials instead of traditional animal leather. Producing animal leather usually involves heavy water consumption, harmful chemicals, and resource-intensive farming. By embracing these plant-based alternatives, we can adopt a more ethical and environmentally mindful approach to fashion, significantly cutting down its ecological impact.
Can eco-friendly leather be used for car interiors and other heavy-duty applications?
Eco-friendly leather has proven to be quite versatile, making it a great choice for items like fashion accessories, footwear, and furniture. However, when it comes to more heavy-duty applications - think car interiors or industrial products - it's still a work in progress. Plant-based options, such as mushroom mycelium or cactus-based leather, are sturdy enough for everyday use but might not yet match the toughness and resistance required for high-stress environments like car seats.
That being said, the durability and performance of sustainable materials are improving steadily. With continuous advancements, eco-friendly leather is on track to become a practical and ethical choice for even the most demanding uses in the near future.
